16 July 2024
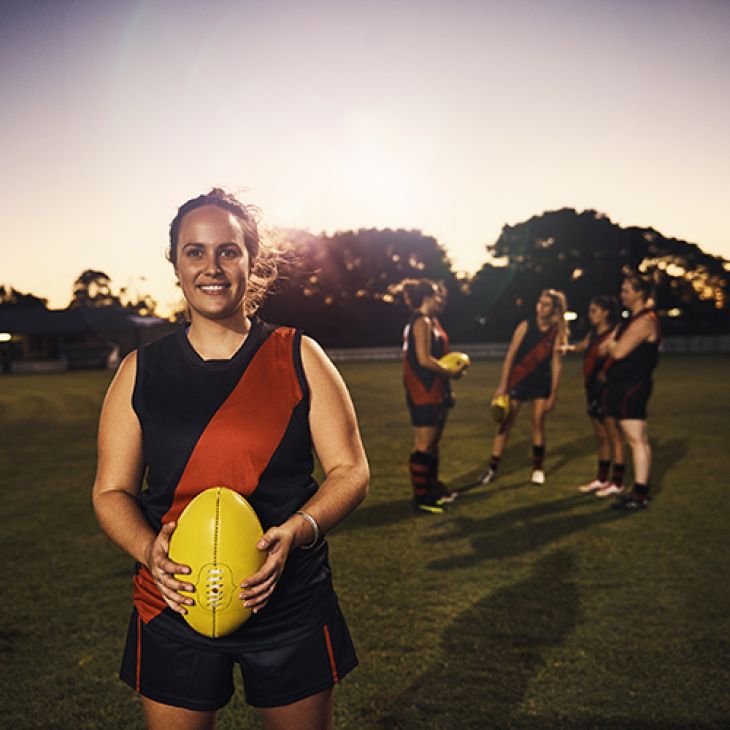
 New research from the University of South Australia has for the first time identified the most common and burdensome injuries experienced by sub-elite female Australian football players in the South Australian National Football League Women’s (SANFLW) competition.
New research from the University of South Australia has for the first time identified the most common and burdensome injuries experienced by sub-elite female Australian football players in the South Australian National Football League Women’s (SANFLW) competition.
The findings show that female Australian football players experience different injury patterns to their male counterparts, highlighting a need for targeted training, injury prevention strategies and potentially match regulation changes.
The paper, published in the Journal of Science and Medicine in Sport found that ankle sprains, concussions, and anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) injuries are the most common, and result in the most missed matches.
424 players from seven teams in the SANFLW were followed over the course of a season, where researchers found that female athletes are at a greater risk for concussion and ACLs than male athletes in the AFL, much like elite AFLW athletes.
This increased risk may be the outcome of physical differences, such as greater joint laxity, or less access to consistent and rigorous Australian football training for women. Female sport nationally and internationally often has less funding to implement injury prevention strategies, which could also contribute to the higher injury rates observed in the SANFLW.
75% of these injuries were the result of contact between players.
Female Australian football has more tackles per-minute of match play than male Australian football, which may suggest a need to review tackling techniques and potentially reduce the amount of contact in matches.
Exercise and Sport Science researcher, UniSA’s Dr Hunter Bennett, says that health practitioners working with female Australian football athletes should consider targeted prevention strategies to reduce the rates of concussion and ACL injuries.
“There should be a focus on neck muscle training to reduce the incidence of whiplash concussion, lower limb neuromuscular control interventions to prevent ACL injuries, and tackling technique training to reduce the overall amount of contact injuries,” Dr Bennett says.
Co-author and Senior Lecturer in Human Movement, Dr Samuel Chalmers, says that female Australian football matches exhibit a different game style, which likely contributes to different injury patterns.
“Female Australian football games are more congested than male games, meaning players contextually do less high-speed running,” Dr Chalmers says.
“The congestion contributes to the high rate of contact injuries. Injury prevention strategies that focus on tackling, falling, and landing techniques, as well as implementing rule changes, could mitigate this and reduce injuries.”
Dr Bennett says this research is the key to preventing injuries in female Australian football players.
“Most injury prevention research has been conducted on male athletes, so there’s been a lack of understanding around injury patterns in females,” Dr Bennett says.
“Understanding the types of injuries that affect female players and how these occur is key to developing targeted strategies to avoid them.”
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Media contacts: Annabel Mansfield E: [email protected] M: +61 479 182 489
Maddie Rawlings E: [email protected]
Researchers: Dr Hunter Bennett E: [email protected]
Dr Samuel Chalmers E: [email protected]